Malta is a captivating country with a rich linguistic heritage that reflects its diverse cultural influences. If you're eager to learn about the official languages spoken in Malta and how they shape the nation's identity, you're in the right place. This article delves into the linguistic landscape of Malta, providing valuable insights into its primary languages and their historical significance.
Nestled in the heart of the Mediterranean, Malta is a small yet vibrant island nation with an extraordinary linguistic history. Over the centuries, Malta has been shaped by various civilizations, including the Phoenicians, Romans, Arabs, Normans, and British, each leaving a lasting impact on its language and culture. Exploring the languages spoken in Malta opens a window into its fascinating past and its enduring cultural richness.
Whether you're planning a visit to Malta, conducting research, or simply curious about the linguistic diversity of this remarkable country, this article offers an in-depth examination of the topic. From official languages and dialects to their roles in education and tourism, we will cover every aspect to provide a comprehensive understanding of Malta's linguistic environment.
Read also:Remembering June Carter Cash A Legendary Figure In Country Music
Table of Contents
- Official Languages in Malta
- The Maltese Language
- English in Malta
- The History of Languages in Malta
- Cultural Influences on the Maltese Language
- Dialects and Variations in Maltese
- The Role of Language in Education
- Language in Malta's Tourism Industry
- The Future of Languages in Malta
- Conclusion
The Dual Linguistic Identity of Malta
Malta boasts two official languages: Maltese and English. Both languages share equal constitutional status, making them indispensable in the daily lives of Maltese citizens. This bilingual policy ensures seamless communication for residents and visitors alike, depending on the context or setting.
The dual presence of Maltese and English highlights Malta's rich history and its strategic location in the Mediterranean. While Maltese serves as a symbol of national identity and cultural pride, English functions as a practical tool for international communication, commerce, and tourism. Together, these languages define Malta's unique linguistic identity.
Why Does Malta Have Two Official Languages?
The existence of two official languages in Malta can be attributed to its complex historical narrative. Maltese, which evolved from the Siculo-Arabic dialect introduced by Arab settlers in the 9th century, represents the nation's deep-rooted cultural heritage. On the other hand, English became prominent during British colonial rule in the 19th and 20th centuries. This dual linguistic legacy continues to shape Malta's identity and influence its society today.
The Unique Charm of the Maltese Language
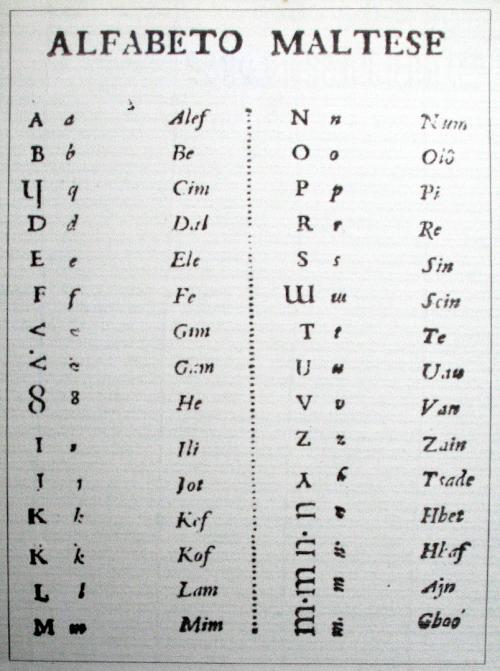
Maltese stands as the national language of Malta and the sole Semitic language written in the Latin alphabet. It is spoken by the vast majority of Maltese residents and serves as a source of national pride. The language's vocabulary draws primarily from Arabic, with significant contributions from Italian, Sicilian, and English.
Maltese is a fascinating blend of linguistic elements, offering a unique glimpse into the island's cultural and historical intersections. For instance, the word "skola" (school) originates from the Italian "scuola," while "il-belt" (the city) traces its roots to Arabic. This rich fusion makes Maltese a captivating subject for linguists and language enthusiasts.
Key Features of the Maltese Language
- Maltese belongs to the Semitic language family, sharing commonalities with Arabic, Hebrew, and other related languages.
- Its alphabet comprises 30 letters, including distinctive characters such as 'ż' and 'ħ.'
- Maltese grammar involves verb conjugations based on subject, tense, and aspect, resembling structures found in Romance languages.
The Essential Role of English in Malta
English plays a pivotal role in Maltese society, functioning as a second official language and a universal medium for international communication. It is widely utilized in government, business, education, and media. A significant proportion of Maltese people are fluent in English, which enhances their ability to engage with global audiences and opportunities.
Read also:Exploring The Financial Empire Of John Cena A Comprehensive Analysis
The widespread use of English in Malta can be traced back to its historical association with the British Empire. During British colonial rule, English was established as the primary language for administration and education. Today, it remains an integral part of Malta's cultural and economic fabric.
How English is Integrated into Daily Life
- Official documents and government communications are often bilingual, featuring both Maltese and English.
- English serves as the primary language of instruction in higher education institutions, equipping students with global competencies.
- Many businesses operate in English to cater to international clients and tourists, reflecting Malta's cosmopolitan nature.
A Journey Through Malta's Linguistic History
The history of languages in Malta is a testament to the island's significance in the Mediterranean. Throughout the centuries, various civilizations have left their linguistic imprints on the Maltese islands, contributing to the evolution of the modern Maltese language.
From the Phoenicians and Romans to the Normans and British, each period of foreign rule introduced new vocabulary and linguistic features. For example, the Arab influence during the 9th to 11th centuries laid the foundation for the Maltese language, while the Italian influence during the Knights of St. John's era enriched its vocabulary in areas such as art, music, and literature.
Key Historical Influences on the Maltese Language
- Arabic: Introduced the core vocabulary and grammatical structure of Maltese.
- Italian: Contributed significantly to the language's lexicon, particularly in cultural domains.
- English: Added modern terminology and technical expressions, especially in fields like technology and business.
The Cultural Richness of the Maltese Language
The Maltese language is a vibrant reflection of the island's cultural diversity. It encapsulates the interactions between various civilizations that have inhabited Malta over the centuries. This cultural fusion has resulted in a language that is abundant in vocabulary and expressive nuances.
Maltese proverbs and idioms often carry traces of its Arab and Italian heritage, offering profound insights into the values and traditions of Maltese society. Moreover, the language continues to adapt, incorporating modern terms and concepts from English and other languages, ensuring its relevance in contemporary times.
Examples of Cultural Expressions in Maltese
- "Ila jgħidu li ma jkunx vero, jkun possibbil" (If they say it's not true, it's possible).
- "Il-bidu jgħidu li l-iskop huwa kollha" (The beginning says that the bishop is everything).
Regional Dialects and Variations in Maltese
While Standard Maltese dominates formal settings, regional dialects and variations enrich the linguistic landscape of Malta. These dialects reflect local traditions and social dynamics, adding depth and diversity to the Maltese language.
For instance, Gozitan Maltese, spoken on the island of Gozo, exhibits distinct phonetic and lexical characteristics compared to the Maltese spoken on the main island. Similarly, rural dialects may differ slightly from urban varieties, showcasing the linguistic diversity within Malta.
Common Dialectal Differences
- Phonetic variations in vowel pronunciation, offering unique regional accents.
- Lexical differences in everyday vocabulary, reflecting local customs and lifestyles.
- Grammatical nuances in sentence structure, highlighting regional linguistic patterns.
The Integral Role of Language in Malta's Education System
Language plays a central role in Malta's education system, with both Maltese and English serving as mediums of instruction. Primary education typically begins with Maltese as the primary language, while English is introduced as a second language. As students advance, the use of English increases, particularly in subjects such as science and mathematics.
This bilingual approach ensures that students develop proficiency in both languages, equipping them with the skills needed for higher education and the global job market. Additionally, foreign languages like Italian, French, and German are often offered as elective subjects, further enhancing students' linguistic capabilities.
Benefits of Bilingual Education
- Improved cognitive abilities and problem-solving skills, fostering intellectual growth.
- Enhanced cultural awareness and global perspective, promoting cross-cultural understanding.
- Increased employability in international industries, opening doors to diverse career opportunities.
Language as a Catalyst for Malta's Tourism Success
Tourism forms a cornerstone of Malta's economy, and language plays a crucial role in its success. The ability to communicate in multiple languages, especially English, ensures that visitors from around the world enjoy a seamless and enjoyable experience. Many hotels, restaurants, and tour operators employ multilingual staff to cater to the diverse needs of their clientele.
Moreover, the Maltese language itself adds charm and authenticity to the tourist experience. Visitors often appreciate the opportunity to learn a few Maltese phrases, deepening their connection to the local culture and traditions.
How Language Elevates Tourism
- Facilitates smooth and effective communication between locals and tourists, enhancing satisfaction.
- Enriches cultural exchanges and understanding, fostering meaningful interactions.
- Boosts Malta's reputation as a welcoming and accessible destination, attracting more visitors.
The Evolving Role of Languages in Malta's Future
As Malta continues to grow and evolve, the role of language in its society will remain dynamic. The increasing globalization and digitalization of the world present both challenges and opportunities for the preservation and promotion of the Maltese language.
Efforts are underway to ensure that Maltese remains vibrant and relevant in the modern era. Initiatives such as language preservation programs, digital resources, and cultural events aim to cultivate a deeper appreciation for the national language among younger generations.
Challenges and Opportunities
- Preserving the distinctiveness of Maltese amidst the pressures of linguistic globalization.
- Leveraging technology to enhance language learning and accessibility, making it more engaging for learners.
- Promoting bilingualism as a competitive advantage in the global marketplace, enhancing Malta's economic prospects.
A Linguistic Legacy Worth Celebrating
Malta's linguistic landscape is a captivating blend of history, culture, and modernity. The coexistence of two official languages, Maltese and English, reflects the island's rich heritage and its strategic importance in the Mediterranean. Understanding the languages spoken in Malta offers valuable insights into its identity and potential.
We invite you to explore Malta's linguistic diversity further and appreciate the unique qualities of its languages. Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below, and feel free to explore other articles on our website for more fascinating insights into global cultures and languages.
References:
- Camilleri, J. (2019). The Linguistic Heritage of Malta. Malta University Press.
- European Commission. (2021). Language Policies in Malta. Retrieved from ec.europa.eu.
- Malta National Statistics Office. (2022). Language Use in Malta. Retrieved from nso.gov.mt.